We dig into the complexities of elbow discomfort and difficulties in this detailed guide. Our goal is to provide you with a complete awareness of this prevalent problem, as well as preventive and treatment techniques. We have you covered whether you’re an athlete battling with overuse injuries or just looking for relief from regular pain.
Elbow Pain Explained
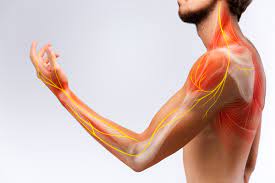
The Elbow’s Structure
To properly treat elbow discomfort, it is essential to understand the complexities of the elbow joint. The elbow is made up of three main bones: the humerus, radius, and ulna. It is a hinge joint that allows for fundamental motions such as arm flexion and extension. Muscles, tendons, and ligaments surround this joint, allowing it to move.
Common Elbow Pain Causes
Elbow discomfort may be caused by a variety of factors, each of which necessitates a unique treatment plan. Among the most prevalent offenders are:
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis): This ailment is caused by repeated gripping and wrist motions, producing irritation of the tendons on the outside of the elbow.
Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis): This ailment, like tennis elbow, affects the inner tendons of the elbow as a result of repeated wrist flexion and gripping exercises.
Overuse Injuries: Athletes that engage in heavy lifting, such as pitchers in baseball, often get elbow discomfort as a result of overuse.
Arthritis: Various types of arthritis may cause persistent pain and stiffness in the elbow joint.
Accidents or falls may cause fractures or dislocations of the elbow, resulting in severe discomfort.
- Common Causes of Elbow Pain:
- Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis): This condition is characterized by pain on the outer side of the elbow and is often caused by overuse of the forearm muscles.
- Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis): Similar to tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow causes pain on the inner side of the elbow and is often due to repetitive gripping and wrist flexion.
- Elbow Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons around the elbow can lead to pain, and it’s often associated with activities that involve repetitive arm movements.
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: This condition occurs when the ulnar nerve, which runs along the inner side of the elbow, becomes compressed or irritated, causing pain and numbness in the hand and fingers.
- Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear on the elbow joint can lead to osteoarthritis, which results in pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa sac, a fluid-filled sac that cushions the elbow joint, can cause pain and swelling.
- Elbow Fractures or Dislocations: Trauma or accidents can lead to fractures or dislocations of the bones in the elbow, causing severe pain and requiring medical attention.
- Symptoms of Elbow Pain:
- Pain and tenderness around the elbow joint.
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion.
- Weakness in the forearm or hand.
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers (in cases of nerve compression).
- Swelling and redness in the affected area.
- Difficulty in gripping or holding objects.
Strategies for Prevention
Preventing elbow discomfort is frequently easier than coping with its consequences. Here are some ways to protect your elbows:
Stretching and warming up properly
Perform proper warm-up exercises and stretches before indulging in any physical activity. This helps the muscles and tendons prepare for action, lowering the chance of damage.
Ergonomic Working Environment
Maintaining an ergonomic workstation is critical for office employees. Chairs, keyboards, and desks that are properly positioned may greatly lessen the pressure on your elbows during extended computer usage.
Flexibility and Strength Training
Include strength and flexibility workouts in your workout program. By concentrating on the forearm and wrist muscles, you may improve the stability and resilience of your elbow. Aspadol 150 mg a painkiller for adults, (Tapentadol), is used to treat moderate to severe acute pain. It is used to treat a number of illnesses, such as headaches, fevers, period pain, toothaches, and colds. It effectively soothes your pain when other treatments fall short.
Maintenance of Equipment
If you’re an athlete, examine and repair your equipment, such as tennis rackets or golf clubs, on a regular basis to ensure it’s in good working order. Elbow injuries may be exacerbated by faulty equipment.
- Symptoms of Elbow Pain:
- Pain and tenderness around the elbow joint.
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion.
- Weakness in the forearm or hand.
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers (in cases of nerve compression).
- Swelling and redness in the affected area.
- Difficulty in gripping or holding objects.
- Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Diagnosis often involves a physical examination, medical history review, and sometimes imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound.
- Treatment options may include rest, ice, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in some cases, splints or braces.
- Severe or persistent cases may require injections (e.g., corticosteroids) or surgery.
- Prevention:
- To prevent elbow pain, it’s essential to use proper ergonomics and technique during activities that stress the elbow, such as sports or repetitive work.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises can help maintain elbow joint health.
- Take breaks and avoid overuse of the elbow to prevent strain.
- When to Seek Medical Attention:
- If you experience severe pain, sudden swelling, or an inability to move the elbow, seek immediate medical attention.
- Chronic or worsening elbow pain should also prompt a visit to a healthcare provider.
Treatment Options That Work
When elbow pain starts, immediate and effective treatment is required to keep it from becoming a chronic problem. Here are some tried-and-true strategies for relieving pain:
Ice and rest
Allow your elbow to rest and use ice to minimize inflammation. This is especially useful for acute injuries or chronic disease flare-ups.
Rehabilitation Therapy
A trained physical therapist may design a specific exercise program to strengthen and stretch the muscles around your elbow.
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) may give short-term pain and inflammation relief. However, before using them on a regular basis, see a healthcare practitioner.
Splinting and bracing
Using a brace or splint may give support while also restricting mobility, which is typically good during the healing process.
Injections
Corticosteroid injections may be advised in certain circumstances to relieve inflammation and discomfort. This should, however, be reviewed with a healthcare practitioner. Tapaday 100 mg(tapentadol) pills are used to treat moderate to severe pain, such as toothache, cerebral discomfort, or various joint and muscle disorders.
When Should You Seek Medical Attention?
While many instances of elbow discomfort may be treated at home, it is critical to identify when professional assistance is required. Consult a doctor if you have any of the following symptoms:
Despite conservative therapy, your pain remains or worsens.
You are experiencing arm or hand weakness.
Around the elbow, there is apparent deformity or edema.
You have a history of major elbow trauma.
To summarize
Elbow discomfort and difficulties may be incapacitating, but with the appropriate information and preventive actions, you can manage and even avoid them. Remember that keeping healthy and pain-free elbows requires a comprehensive approach that involves knowledge, prevention, and treatment. If you’re experiencing elbow discomfort, talk to a doctor about a personalized treatment plan. You may recover the health and functioning of your elbow by completing the necessary actions.