https://housedecoring.com/ At its core, a Passive House is a building that is designed to be incredibly energy-efficient without relying on complex mechanical systems. It aims to maintain a comfortable interior climate throughout the year with minimal reliance on traditional heating or cooling methods.
Superb Insulation (H2)
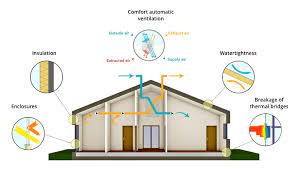
One of the fundamental principles of a Passive House is exceptional insulation. The walls, roof, and floors are meticulously insulated to prevent heat transfer, keeping the interior cozy in the winter and cool in the summer.
Airtight Construction (H2)
Passive Houses are constructed with airtightness in mind. Special attention is paid to sealing gaps and cracks to minimize air leakage, ensuring that the indoor environment remains stable and comfortable.
High-Performance Windows and Doors (H2)
To optimize energy efficiency, Passive Houses feature high-quality, triple-glazed windows and well-insulated doors. These components minimize heat loss and contribute to the overall thermal comfort of the building.
The Role of Ventilation (H1)
Controlled Ventilation (H2)
While airtightness is a key aspect, Passive Houses are not hermetically sealed. They incorporate a mechanical ventilation system with heat recovery to ensure a constant supply of fresh air without compromising energy efficiency.
Heat Recovery (H2)
The ventilation system plays a crucial role in recovering heat from the outgoing air, pre-warming the incoming fresh air. This heat exchange significantly reduces the need for additional heating during colder months.
Achieving Net-Zero Energy (H1)
Minimal Energy Demand (H2)
Thanks to its design and insulation, a Passive House requires remarkably little energy for heating and cooling. This minimal energy demand can often be supplied by renewable energy sources like solar panels.
Sustainable Energy Sources (H2)
To achieve a net-zero energy balance, Passive Houses often integrate renewable energy solutions. Solar panels, wind turbines, and other green technologies are commonly employed to meet energy needs.
Benefits of Living in a Passive House (H1)
Exceptional Comfort (H2)
Passive Houses offer an exceptional level of comfort, with stable temperatures, consistent fresh air, and minimal drafts. The indoor environment is incredibly pleasant year-round.
Drastic Energy Savings (H2)
Residents of Passive Houses enjoy substantial energy savings, leading to lower utility bills. The reduced energy consumption also has a positive impact on the environment by lowering carbon emissions.
Sustainability (H2)
By relying on renewable energy sources and minimizing energy consumption, Passive Houses contribute significantly to sustainability efforts and combat climate change.
The Future of Sustainable Living (H1)
As we strive to reduce our carbon footprint and create a more sustainable future, Passive Houses represent a promising solution. Their innovative design and focus on energy efficiency are paving the way for a new era of construction that prioritizes environmental responsibility and human well-being.
Permission is granted to publish this article electronically in free-only publications, like a website or ezine (print requires individual permission) as long as the resource box is included without any modifications. All links must be active. A courtesy copy is requested on publication.
In passive house design, the cost savings that result from dispensing with the conventional heating system can be used to pay for the upgrading of the building envelope and provide renewable energy heating. If you are planning to build your own passive house then it is essential that you know as much as possible about passive house design. Passive houses are very well insulated, virtually airtight, buildings which minimize energy loss and improve occupant comfort. Passive house design considers the entire life-cycle of the building and uses a variety of ‘passive’ building solutions to eliminate conventional ‘active’ technologies that consume wasteful fossil fuels.
Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design is specifically used to exploit free energy from the sun, to provide warmth. A passive house is orientated so that large south facing windows absorb energy from the sun. The rooms are laid out so that the solar heat is distributed from these windows through the interior of the home. The process of capturing the solar energy is considered to be ‘passive’, since the building does not generate the energy itself. The heat energy comes from a natural source and is not generated exclusively by artificial means.
Provide Thermal Mass
Passive house buildings can be constructed from either dense or lightweight materials. In the case of lightweight construction, like timber frame, some internal thermal mass is incorporated. Thermal mass allows dense construction materials, typically concrete, stone, brick or tile, to store the free heat. During the day, when external temperatures are highest, a large thermal mass inside the insulated envelope will absorb the sun’s heat. When the external temperature cools down in the evening, the thermal mass will naturally radiate that absorbed heat throughout the rooms.
Install Super Insulation
Insulating the building envelope is one of the most important passive house measures as it has the greatest impact on energy expenditure. In the average house, well considered and expertly installed insulation can reduce the amount of heat lost through the building envelope, by at least half. In addition, a high standard of thermal insulation will considerably improve thermal comfort for the building occupants.
Make the Building Airtight
Effective airtightness is another important contributor to passive house design. Warm air leaking from the building is a major cause of heat loss, which results in wasted energy. Improving the building’s airtightness reduces the uncontrolled air flow through gaps and cracks in the building fabric and must be addressed by the designer early in the planning process.
Fit Triple Glazed Windows
High performance windows are a key contributor to the overall efficiency of the building envelope, as they are manufactured to deliver high thermal values. In passive house buildings, it is usual to combine triple-pane insulated glazing, low emissivity (low-E) glass and argon or krypton filled air gaps. Expertly designed and installed triple glazed windows will significantly reduce energy usage and improve occupant comfort.
Make Use of Waste Heat
In addition to using passive solar heating, passive houses make use of the waste heat from lighting, domestic appliances like refrigerators and washing machines, and the body-heat from the occupants of the building.
Install Heat Recovery Ventilation
Heat recovery ventilation is the process of exchanging heat energy contained in the air which is extracted from a house and transferring it to the incoming replacement air. This system can comprise either a central extract system or individual room fans. Although this ventilation method is an ‘active’ technology, using a small amount of electricity, it is considered to be a worthwhile contributor to energy saving. It provides the building with essential fresh air, improves occupant comfort and conserves the building’s heat. https://framespot.co.uk/shop-best-frames-in-uk/
Fit Renewable Energy Heating
An underlying objective of solar passive design is the desire to dispense with conventional heating systems altogether. It is usually necessary to provide some supplementary space heating to maintain comfortable conditions on particularly cold winter days. Often this can be achieved via the low volume heat recovery ventilation system that is provided to maintain air quality. As an alternative to this, a renewable energy technology like a wood burning stove, solar heating, air source heat pumps or ground source heat pumps, may be preferred.