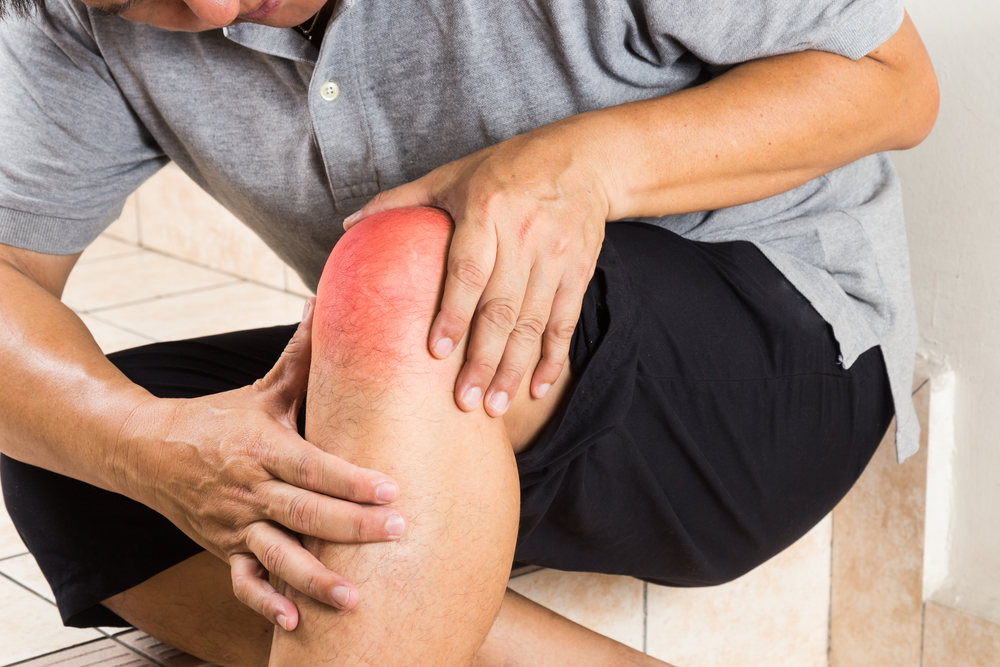
The word inflammatory is often used in health contexts, although its meaning is not always apparent. Infections, damaged cells, and irritants are just a few examples of the various stimuli that can cause inflammation in a biological system. This complicated process acts as the body’s defensive system, attempting to remove toxic chemicals and begin the healing process. However, inflammation may emerge in a variety of ways, with both acute and chronic consequences that require investigation.
Tapentadol 200mg is a larger dose of the medicine used to treat moderate to severe pain. Tapentadol 200mg, like the 100mg dosage, is an opioid analgesic. Its mode of action includes binding to the mu-opioid receptor and blocking norepinephrine reuptake, resulting in dual pain relief benefits.
The Physiology of Inflammation
Inflammatory reactions are coordinated processes that include immune cells, cytokines, and signaling pathways. When the body detects a danger, it sends immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, to the site of damage or infection. These cells produce inflammatory mediators, including cytokines such as interleukins and tumor necrosis factor, which control immune function and promote tissue healing.
Acute vs Chronic Inflammation
Acute inflammation is a quick and limited reaction that usually resolves within a few days. It causes traditional symptoms such as redness, swelling, heat, and pain and serves as an important defensive mechanism against infections and injuries. Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, lasts for a long time and is often low-grade and systemic in character. It may be caused by a variety of reasons, including chronic infections, autoimmune illnesses, or lifestyle choices such as a poor diet and stress.
Tapentadol 100mg is a medicine used to relieve moderate to severe pain. It is an opioid analgesic. The major method of action is to bind to the mu-opioid receptor and impede norepinephrine reuptake. This multimodal mechanism helps manage pain by influencing both the opioid and noradrenergic pathways.
The Role of Inflammatory Diseases
Understanding inflammatory processes is critical, given their impact in a variety of disorders. Rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma all result from dysregulated inflammatory responses, which cause tissue damage and functional impairment. Furthermore, accumulating evidence shows that chronic inflammation leads to the development of a variety of diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and some malignancies.
The implications for health and wellness
Inflammation has a wide-ranging impact on health and well-being. Lifestyle variables such as nutrition, exercise, and stress management have a significant influence on inflammatory pathways. A diet high in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may assist to lower inflammation and illness risk. Similarly, regular physical exercise and stress-reduction practices such as meditation and yoga have anti-inflammatory benefits, which promote overall health.
Buy tapentadol online is a centrally acting analgesic (pain reliever) that treats moderate to severe pain. It is classed as an opioid analgesic and comes in both immediate and extended-release forms. Tapentadol binds to mu-opioid receptors in the central nervous system and inhibits norepinephrine reuptake.
Strategies to Manage Inflammation
Individuals with knowledge may take proactive steps to regulate inflammatory processes and protect their health. Consuming anti-inflammatory foods such as berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish may help to control inflammatory pathways and improve general health. Furthermore, regular exercise and stress reduction strategies may help to combat inflammatory tendencies and promote a healthy physiological condition.
Harnessing the Power of Nutraceuticals
Nutraceuticals provide promise for inflammation treatment in the domain of holistic health. Natural chemicals such as curcumin, found in turmeric, and resveratrol, found in red grapes, have powerful anti-inflammatory activities. Individuals may improve inflammatory management by including these substances into their health program.
FAQS
- What is inflammation?
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, irritants, or damaged cells. It is a protective mechanism that helps the body fight off infection and promote healing. - What causes inflammation?
Inflammation can be triggered by various factors, including infections, injuries, autoimmune disorders, unhealthy lifestyle choices (such as a poor diet or lack of exercise), chronic stress, and environmental toxins. - What are the different types of inflammation?
Inflammation can be classified into two main types: acute inflammation, which is short-term and typically resolves within a few days, and chronic inflammation, which persists over a prolonged period and can contribute to various health issues. - What are the common signs and symptoms of inflammation?
Common signs and symptoms of inflammation include redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and loss of function in the affected area. Systemic inflammation may also manifest as fatigue, fever, headache, and overall malaise. - How is inflammation diagnosed?
Inflammation can be diagnosed through a combination of medical history review, physical examination, laboratory tests (such as blood tests, imaging studies, and biopsies), and assessment of symptoms. - How is inflammation treated?
Treatment for inflammation depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. It may include lifestyle modifications (such as adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise routine), medications (such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressants), physical therapy, and complementary therapies (such as acupuncture or herbal remedies). - Can inflammation be prevented?
While some causes of inflammation are beyond our control, adopting a healthy lifestyle can help prevent or reduce inflammation. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, staying physically active, managing stress, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and getting regular check-ups. - When should I seek medical attention for inflammation?
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience severe or persistent symptoms of inflammation, such as intense pain, swelling, fever, or difficulty breathing. Additionally, if you have a chronic inflammatory condition, it is essential to follow up with your healthcare provider regularly to monitor your condition and adjust treatment as needed. - Can inflammation affect long-term health?
Yes, chronic inflammation has been linked to various long-term health issues, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, autoimmune disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain types of cancer. Managing inflammation through lifestyle changes and appropriate medical treatment is crucial for preserving long-term health and well-being. - Where can I find more information about inflammation?
You can find more information about inflammation from reputable sources such as medical websites, research journals, healthcare organizations, and healthcare providers. Additionally, discussing any concerns or questions with your healthcare provider is always advisable for personalized guidance and support.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inflammatory processes are a complex interplay of biological reactions that have far-reaching consequences for health and illness. Individuals may empower themselves by learning the complexities of inflammation and using proactive ways to reduce inflammatory risks and develop robust well-being. With a comprehensive approach that includes diet, lifestyle, and tailored therapies, we may traverse the inflammatory terrain with resilience and energy.