High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common but serious health condition affecting millions worldwide. It’s often called the “silent killer” because it can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems without any noticeable symptoms. Given the potential risks associated with high blood pressure, regular heart check-ups are crucial for individuals with this condition. In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into what you need to know about heart checkups in patiala, why they are essential for people with high blood pressure, and what to expect during these check-ups.
Understanding High Blood Pressure
What is High Blood Pressure?
High blood pressure occurs when the force of blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. It’s typically measured in systolic pressure (the force when your heart beats) and diastolic pressure (the force when your heart is at rest). High blood pressure is defined as a reading of 130/80 mm Hg or higher.
Complications of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for various health complications, including:
- Heart Disease: Hypertension can lead to the thickening of the heart muscle, increasing the risk of heart attacks, heart failure, and other heart-related conditions.
- Stroke: Elevated blood pressure can damage blood vessels in the brain, increasing the likelihood of strokes.
- Kidney Damage: High blood pressure can affect the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney disease or failure.
- Eye Problems: Hypertension can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, potentially causing vision problems or blindness.
- Aneurysms: Weak spots in blood vessel walls can form aneurysms, which can rupture and be life-threatening.
Why Heart Check-Ups Are Vital for Those with High Blood Pressure
Monitoring Blood Pressure Levels
Regular heart check-ups are essential for people with high blood pressure to monitor their blood pressure levels. Monitoring helps healthcare providers assess how well the condition is being managed and whether adjustments to treatment are needed.
Assessing Heart Health
Heart check-ups involve a series of tests and evaluations to assess the overall health of your heart. These assessments can identify early signs of heart disease or other cardiac conditions.
Identifying Risk Factors
Heart check-ups also help identify other risk factors that can contribute to heart problems. By addressing these risk factors, such as high cholesterol, diabetes, or obesity, individuals can reduce their overall cardiovascular risk.
Frequency of Heart Check-Ups
Initial Assessment
An initial heart check-up is typically recommended for individuals newly diagnosed with high blood pressure. This assessment establishes baseline measurements and provides a comprehensive view of heart health. The frequency of these initial check-ups may vary depending on the severity of hypertension and the individual’s overall health.
Ongoing Monitoring
After the initial assessment, individuals with high blood pressure should undergo regular monitoring as their healthcare provider advises. Typically, these check-ups occur at least once a year, but more frequent visits may be necessary for those with uncontrolled hypertension or additional risk factors.
What to Expect During a Heart Check-Up
During a heart check-up, your healthcare provider will perform various tests and evaluations to assess your heart health. Here’s what you can expect:
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your healthcare provider will review your medical history and perform a physical examination. They’ll ask about your lifestyle, family history, and any symptoms or concerns you may have.
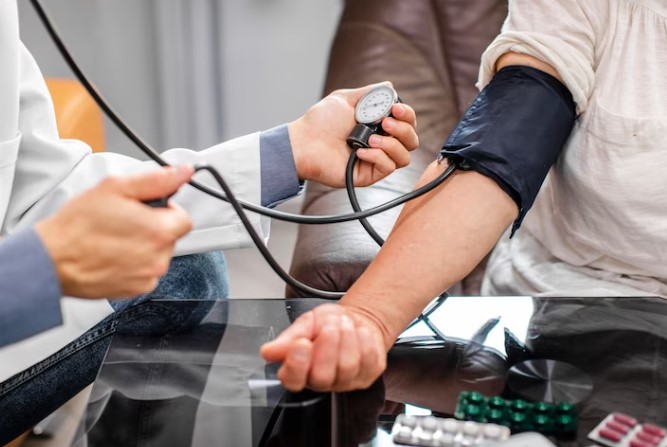
Blood Pressure Measurement
Regular blood pressure measurement is a fundamental part of a heart check-up for people with hypertension. Your healthcare provider will use a blood pressure cuff and stethoscope or an automatic blood pressure monitor to record your systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Blood Tests
Blood tests, including a lipid profile, can help assess cholesterol levels in your blood. Elevated cholesterol levels are a risk factor for heart disease.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
An ECG records the electrical activity of your heart. It can detect irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) and other heart-related abnormalities.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart. It provides images of the heart’s structure and function, allowing healthcare providers to assess the heart’s pumping capacity, valve function, and overall health.
Stress Test
A stress test on a treadmill or stationary bike evaluates how your heart responds to physical stress. It helps identify coronary artery disease and assesses your heart’s endurance.
Holter Monitor
A Holter monitor is a portable device that continuously records your heart’s electrical activity over a 24 to 48-hour period. It helps diagnose irregular heart rhythms that may not show up during a brief ECG.
Additional Tests as Needed
Your healthcare provider may recommend additional tests or imaging studies based on your individual risk factors and symptoms.
Interpreting Test Results
Understanding the results of your heart check-up is crucial for managing your high blood pressure and overall heart health. Here’s what key test results mean:
Blood Pressure Readings
Blood pressure readings will indicate whether your hypertension is controlled or if adjustments to your treatment plan are necessary.
Lipid Profile
Your lipid profile measures cholesterol levels, including LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and HDL (“good”) cholesterol. High LDL cholesterol levels are a risk factor for heart disease.
Electrocardiogram
An ECG will show the electrical activity of your heart. Abnormalities may be detected, such as irregular heart rhythms or signs of previous heart attacks.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram provides a detailed view of your heart’s structure and function. Any abnormalities in the heart’s chambers, valves, or overall function will be identified.
Lifestyle Modifications for Managing High Blood Pressure
Diet and Nutrition
A heart-healthy diet low in salt, saturated fats, and cholesterol can help manage high blood pressure. It includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and limited processed foods.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling can help lower blood pressure and improve overall heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Medication Management
If lifestyle changes alone are insufficient to control high blood pressure, medications may be prescribed. Adhering to your prescribed medications is essential for managing hypertension effectively.
Stress Reduction
Stress can contribute to high blood pressure. Practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and support heart health.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Heart Health with Regular Check-Ups
Heart health check-ups are fundamental to managing high blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart-related complications. For individuals with hypertension, these regular assessments provide valuable information about the condition of the heart and overall cardiovascular health. By monitoring blood pressure, assessing heart function, and identifying risk factors, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to individual needs, helping individuals with high blood pressure lead healthier lives and reduce their risk of heart disease and related complications.
Looking for a heart specialist in Patiala? Contact us today to know more.